- HOME >
- Service >
- Electrode Services >
- Selection of Use
Selection of Use
| Process | Electrode type | Typical size | Recoating availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caustic soda and caustic potash production |
|
× | |
| Sodium chlorate (chlorate) production |
|
○ | |
| Sodium hypochlorite production |
|
△ | |
| Seawater electrolysis |
|
△ | |
| Zinc, zinc alloy plating (EGL) |
|
○ | |
| Tin plating (ETL) |
|
○ | |
| Copper plating |
|
○ | |
| "Electrolytic Pickling, Pretreatment for Steel plating Electrolytic Pickling" |
|
○ | |
| Copper foil (used in copper plating) |
|
○ | |
| Surface conversion treatment of aluminum foil |
|
△ | |
| Electrolytic extraction and recovery of indium, precious metals, etc |
|
○ | |
| Electrolytic extraction of copper, nickel, cobalt and other nonferrous metals |
|
○ | |
| Electrolysis of sodium sulfate |
|
△ | |
| Organic Compound Electrolytic Synthesis |
|
○ | |
| Plating auxiliary electrode |
|
× | |
| Various types of plating (including chrome plating) |
|
○ | |
| Hypochlorite water, alkaline ionized water production |
|
× | |
| Electrodeposition coating |
|
○ | |
| Wastewater Electrolysis Treatment |
|
△ |
Shape Image
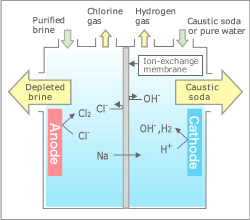
Brine Electrolysis
For use as base chemical materials. Produces chlorine gas from an anode chamber and caustic soda and hydrogen gas from a cathode chamber.
Ion exchange membrane type-brine electrolysis is a process that simultaneously produces chlorine gas, caustic soda and hydrogen gas by the use of direct electric current through an electrolysis cell with an ion exchange membrane installed between the anode and the cathode. In this process, super-purified sodium chloride brine is fed to the anode chamber, whereas pure water and return caustic soda or sodium hydroxide solution, is fed to the cathode chamber.
Seawater Electrolysis
For seawater intake purposes. Produces sodium hypochloride by direct electrolysis of seawater.
Seawater electrolysis is a direct electrolysis process of seawater used to generate chlorine gas on the anode side and sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas on the cathode side and then to produce sodium hypochlorite through immediate reaction under the seawater. The sodium hypochlorite produced from this process is useful to curtail the breeding activities of various creatures and shells living in the seawater and thereby to prevent sticking and clogging by such seawater creatures inside seawater intake pipes.
Electroplating (general)
For purposes of corrosion resistance or decoration. Plating of various metals onto base materials.
Electroplating is a method used to industrially coat the surface of a base material with a different metal, such as, copper, gold, nickel or chrome to improve the corrosion resistance of the plating material or to provide decoration. In this case, the base material functions as a cathode, whereas the counter electrode functions as an anode and generates oxygen gas.
Electrogalvanizing Electro Tin Plating
For corrosion resistance purposes. Plating of zinc or tin onto plating materials.
Electrogalvanizing is a method used to industrially coat the surface of a steel plate with zinc or tin to improve the corrosion resistance of a steel plate. In this case, the steel plate for plating functions as a cathode, whereas the counter electrode functions as an anode and generates oxygen gas. The electrogalvanizing of steel plates with zinc is used for the manufacturing of automobiles and electrical appliances, whereas the electroplating with tin is used for food/beverage cans, drums, and bottle caps in addition to electrical parts.
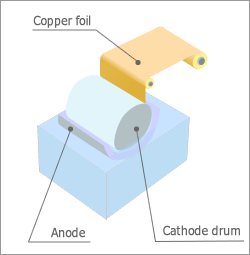
Electrolytic Copper Foil Process
Produces copper foils by electrolyzing copper ion-containing electrolytes, for printed electro circuits.
There are two different ways to manufacture copper foils. The first is an electrolysis method, and the other is a rolling method. The rolling method is a process by which copper foils are manufactured by repeated rolling and annealing of copper, and as a result, this particular method includes restrictions to the length and width of the product foil. Conversely, the electrolysis method is a process used to manufacture thinner copper foils than those obtained by the first method and involves electrolyzing copper ion-containing electrolyte in an electrolytic cell. Thus, in this method, there are few restrictions to the product foil. The electrolysis method is better fitted for the manufacture of thinner cooper foils and is widely used for the manufacturing of various advanced electronic devices, such as, lithium ion batteries and flexible-printed circuit boards.
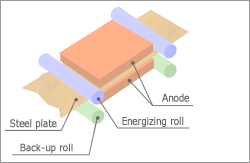
Electrolytic Pickling
Removes mill scale created on the surface of a steel strip through electrolysis.
Electrolysis pickling is a process used to remove mill scales created on the surface of a steel strip through electrolysis by passing the steel strips though a neutral or acidic salt solution.
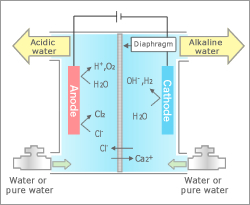
Water Electrolysis
Generates acidic water and alkaline water, mainly for cleaning purposes, through direct electrolysis of water.
Water electrolysis is a process used to generate anti-bacterial and environmentally friendly acidic and alkaline water with high cleaning power through membrane electrolysis of natural or tapped water with a small amount of additives. The produced water is widely used for such purposes as medical treatment and welfare, hygiene, agriculture and food, including the products for daily use, such as, deodorants, cleaning agents and health products.
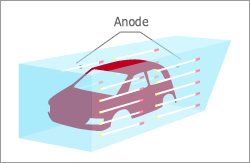
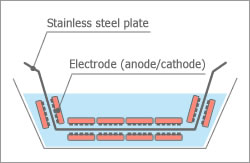
Electrodeposition
Helps to evenly coat a metal body with direct current while bathed in water solution or water dispersion paint.
Electrodeposition is a process used to evenly coat a metal body with organics and is used for industrial painting, such as, car bodies and building materials. In this process, a direct electric current is applied, while the item to be painted is bathed in water or water dispersion paint.